ECONOMIC KNOWLEDGE
What is the Federal Reserve(Bank) System?
Edited by Stephen Lee with CRI
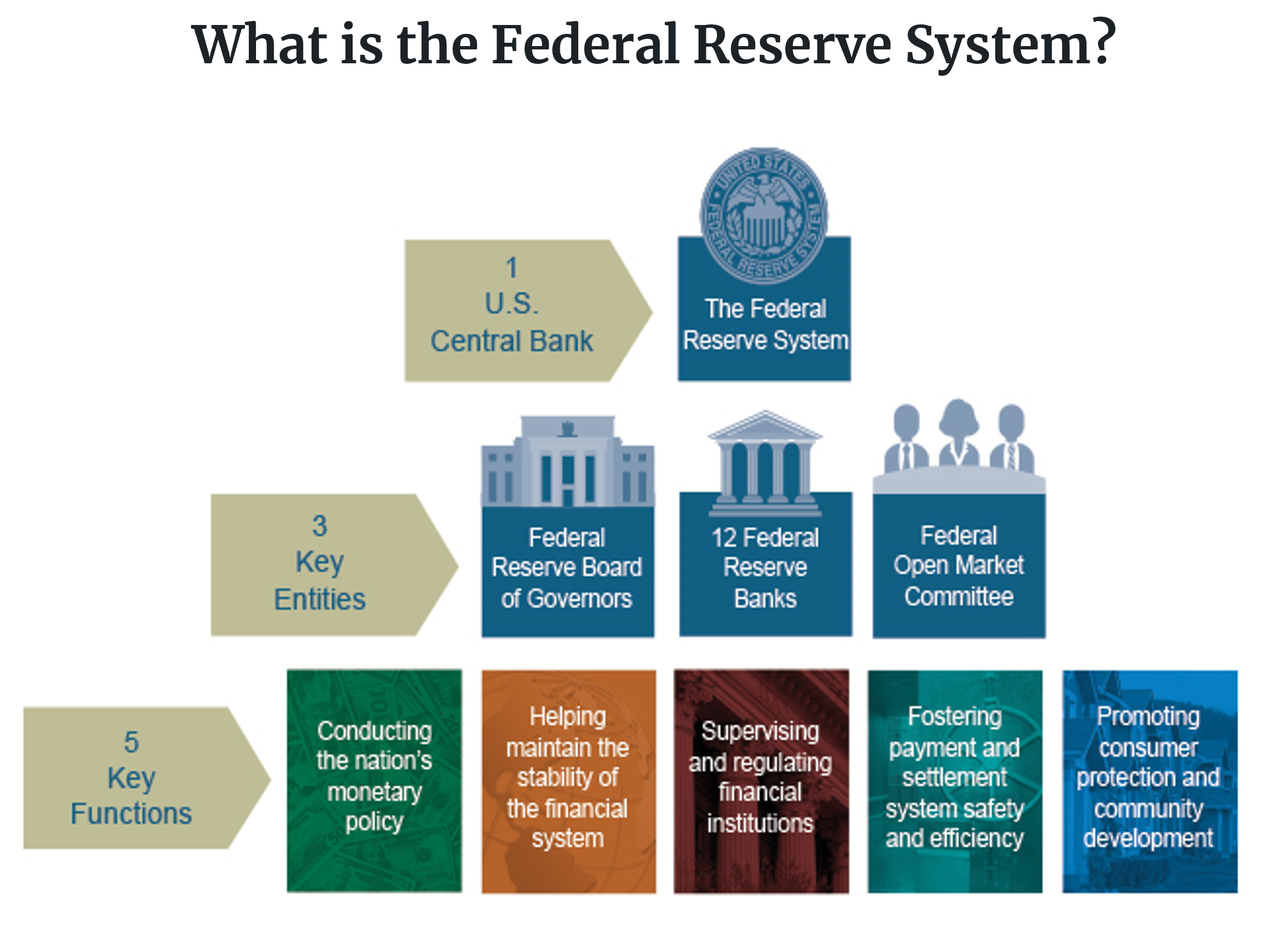
1. Definition of the Federal Reserve System
- The central banking system of the U.S. of America, which is the most powerful economic institution in the U.S., perhaps the world. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, signed by President Woodrow Wilson, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises.
2. Who is the Federal Reserve Bank(the Fed) owned by?
- The Federal Reserve Banks are NOT a part of the federal government, but they exist because of an act of Congress.
- Their purpose is to serve public. So is the Fed private or public? The answer is both. While the Board of Governors is an independent government agency, the Federal Reserve Banks are set up like private corporations.
3. What does the Federal Reserve Bank do?
1) Conducts the nation’s monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the U.S. economy.
2) Promote the stability of the financial system and seeks to minimize and contain systemic risks
3) Promotes the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions and monitors their impact on the financial systems as a whole
4) Fosters payment and settlement system safety and efficiency through services to the banking industry and the U.S. government that facilitate U.S. dollar transaction and payment
5) Promotes consumer protection and community development through consumer-focused supervision and examination, research and analysis of emerging consumer issues and trends, community economic development activities, and the administration of consumer laws and regulations.
4. Organization of the Federal Reserve
There are three key entities in the Federal Reserve System:
1) The Board of Governors : 7 members
They are appointed by the president of The U.S. and confirmed by the Senate for staggered 14-year terms.
They are led by the chair and vice chair whose term is 4 year and can be re-appointed once.
2) The Federal Reserve Banks : 12 presidents
12 Federal Reserve District boundaries are based on economic considerations; the Districts operate independently but under the supervision of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors.
Boston New York Philadelphia Cleveland Richmond Atlanta
Chicago St. Louis Minneapolis
Kansas City Dallas San Francisco
3) The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) : 12 members
It is the Fed’s monetary policymaking body who manages the
nation’s money policy. FOMC schedules 8 meeting a year.
-
- 7 members of the Board of Governors of the Fed
- The president of Fed Reserve Bank of New York
- Four of the remaining eleven Reserve Banks presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.

4) How is a Fed Chair selected ?
By law, the president nominates a Fed Chair and two Vice Chairs for four-year terms and must be confirmed by the Senate. Jerome Powell was confirmed for a second four-year term as chair on May 12, 2022.